 Aina Frau-Pascual
Aina Frau-Pascual
I am a research scientist with an interest in signal processing, machine learning and data analysis in healthcare, with experience in brain imaging research
MGH/HMS, Boston, MA
Analysis of datasets with traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients and controls, to find differences in connectivity and identify the main hubs that affect consciousness. Collaborations in the context of this work led to several journal publications, that can be found here and here.
MGH/HMS, Boston, MA
Acquisition of functional MRI data in the 7T scanner and analysis of the data to find differences between subjects with cerebral amyloid angiopathy and healthy subjects. This project led to the publication of a journal paper and of an OHBM 2021 abstract.
MGH/HMS, Boston, MA
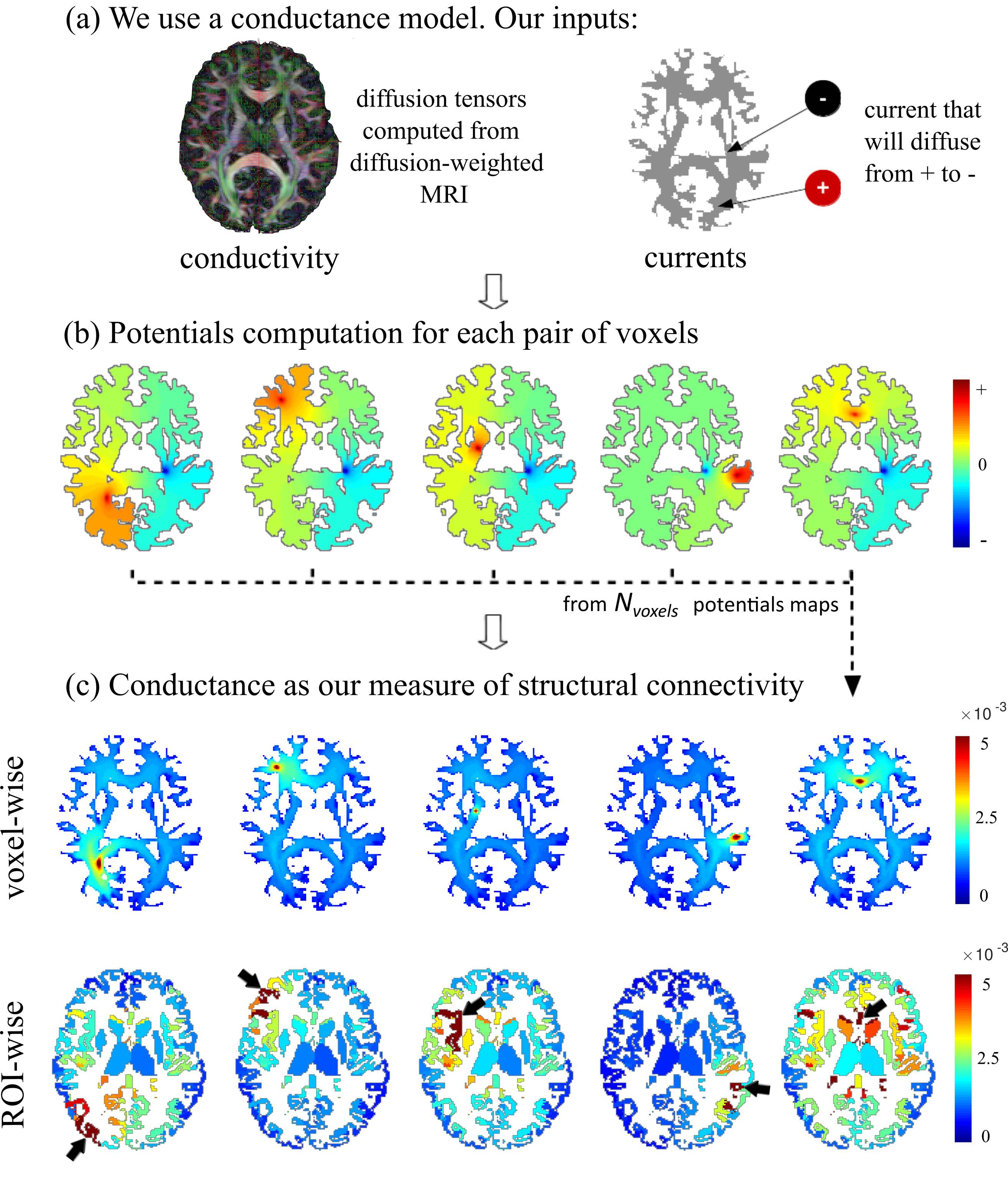
Development of a global method that quantifies structural brain connectivity derived from diffusion MRI, with the use of a conductance model. Detecting structural brain connectivity differences in disease. Here you can find the paper and code. This method has been also used in the study of aging and Alzheimer's disease data, and the results were presented at the 2019 Asilomar and the 2020 ISBI conferences. The consequent journal paper can be found here.
Inria, Grenoble and Paris, France
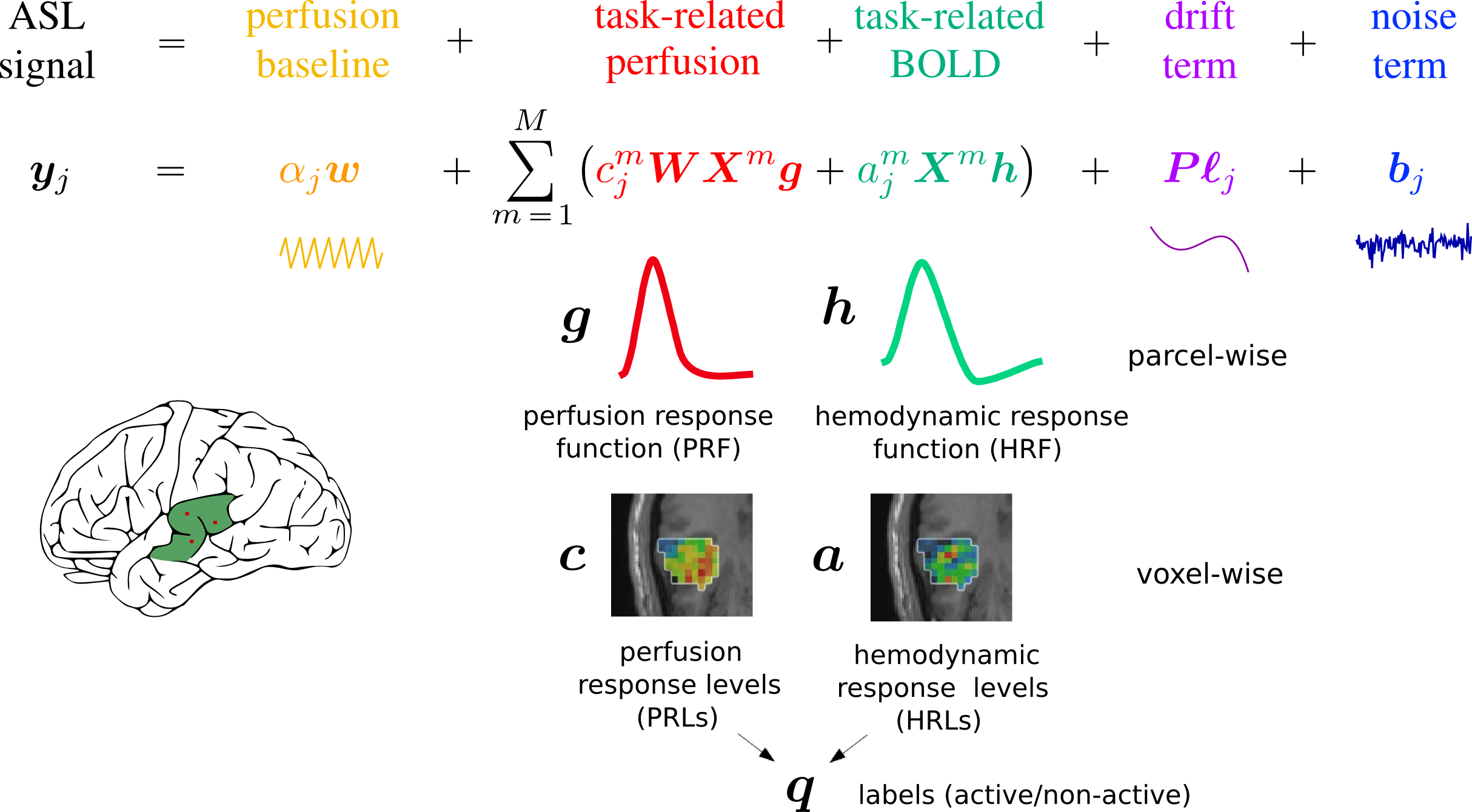
Statistical Models for the coupling of ASL and BOLD Magnetic Resonance modalities to study brain function and disease. It included: the creation of a parcellation of the brain based on hemodynamic features extracted from BOLD fMRI (paper can be found here); the inclusion of a physiological prior to inform a Bayesian analysis of ASL fMRI data (paper can be found here); the comparison of multiple physiological models and parameters in the analysis of ASL fMRI data (paper can be found here); and the development of stochastic and variational solutions to ASL fMRI data analysis (paper can be found here). Codes are available at pyhrf.github.io
CEA Neurospin, Inria-Saclay, France
Development of a non-parametric joint estimation method for functional MRI task activation values and the hemodynamic response function (HRF). The HRF was modeled as a Gaussian Process, making continuous evaluation possible. The paper can be found here.